Page 59 - Year 10
P. 59
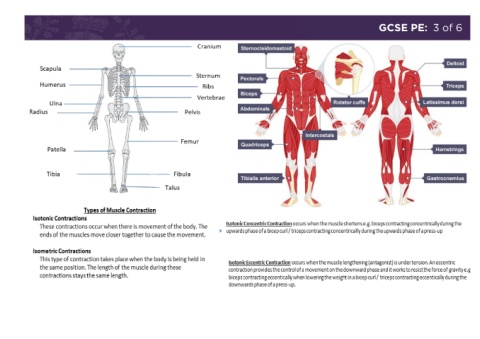
GCSE PE: 2 of 6 GCSE PE: 3 of 6
Calories: Factors that effect calorie intake:
Energy is measured in calories. These calories are Age – younger people need more calories to help them grow. After 25 the calorie needs of individuals starts to fall.
obtained from the food and drink we consume. Gender – Men need more calories that women.
Male = 2500 kcal/day Female = 2000 kcal/day Height – The taller an individual the more calories they require.
Energy Expenditure – The more exercise an individual does the more calories they need.
Maintaining Weight: Calories Taken in = Calories Used Basal Metabolic Rate – This is now fast energy is being used and varies from individual to individual.
Weight Gain: Calories taken in is more that calories
used
Weight Loss: Calories taken in is less that calories used
What is a balanced diet?
Eating the right amount of calories to deal with the energy that will be needed. It is also eating different food types
to provide the body with the right nutrients, vitamins and minerals to remain healthy.
Somatotypes (body shapes) Ideal average intake of main nutrients – Carbohydrates = 55 – 60%, Fat = 25 – 30%, Protein = 15 – 20%
Ectomorph:
• Very thin, lean and usually tall
• Narrow shoulders, hips and chest Why should we strive to have a balanced diet?
• Not much fat / muscle • Unused energy is stored as fat which could lead to obesity.
• Long arms and legs • The human body needs nutrients for energy, growth and hydration.
Activities that suit ectomorphs:
• High Jump / Pole Vault – lighter so less weight to lift in the air over the
bar.
• Marathon runner / Long distance runners – Lighter so less weight to carry
+ longer stride length so can cover larger distance with each stride.
Mesomorph: Carbohydrates: Protein: Fats:
• Broad shoulders and thin waist (narrow hips) Bodies main energy source especially Food source which is used for growth and Food source that provides energy at low
• Large amount of muscle during exercise. repair of body tissues. intensities.
• Strong arms and thighs Simple Carbohydrates – stored as Fat can provide more energy than
• Little body fat
Activities that suit mesomorphs: glucose and is broken down quickly Athletes would require power / strength / carbohydrates BUT only when the
• Sprinting – large arms and legs to help produce more power resulting in for fast energy release (found in sugar speed need protein to help their muscle performer is working at a low intensity.
them running quicker. food e.g. sweets). development (growth) and repair of muscle Often used for energy when walking or
• Weightlifter – Large muscles helps provide the force required to lift heavier Complex Carbohydrates – stored as tissue after training sessions (micro tears). jogging and is also used when a runner
weights starches in the body and are broken has used up all their carbohydrate stores
• Rugby player – Muscle helps generate force required when making contact down more slowly but produce large Protein can also be used as an energy (starches).
with opponents.
amounts of energy (found in bread, source at the end of prolonged activities
Endomorph: pasta and potatoes). when all other energy sources have been Unsaturated fats cause cholesterol which
• High content of fat used up. leads to the narrowing of arteries and can
• Fat round middle, thighs and upper arms cause heart attacks.
Activities that suit endomorphs:
• Sumo-wrestling – large size is difficult to force out of the ring and can be
used to create short powerful actions.
• Shot Putter – Extra bulk allows for a more powerful release of shot.