Page 49 - Year 11
P. 49
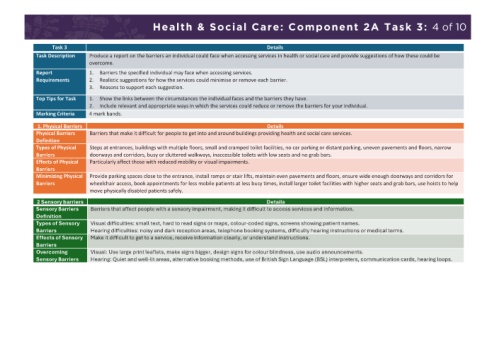
Health & Social Care: Component 2A Task 2: 3 of 10 Health & Social Care: Component 2A Task 3: 4 of 10
Task 2 Details Task 3 Details
Task How social care services meet the needs of an individual Task Description Produce a report on the barriers an individual could face when accessing services in health or social care and provide suggestions of how these could be
Objective Produce a report on how social care services can meet the needs of the user overcome.
Report Must Include - How social care services could meet the specific needs of the specified individual. Report 1. Barriers the specified individual may face when accessing services.
- How voluntary care services could meet the specific needs of the specified individual. Requirements 2. Realistic suggestions for how the services could minimise or remove each barrier.
- How informal care options could meet the specific needs of the specified individual. 3. Reasons to support each suggestion.
Top Tips for This Task - Really focus on the needs of your individual Top Tips for Task 1. Show the links between the circumstances the individual faces and the barriers they have.
-Be specific. What needs do they have because of their circumstances and condition? 2. Include relevant and appropriate ways in which the services could reduce or remove the barriers for your individual.
- Remember to include voluntary care and informal care too. Marking Criteria 4 mark bands.
1. Social Care services 1. Physical Barriers Details
Section Details Physical Barriers Barriers that make it difficult for people to get into and around buildings providing health and social care services.
Social Care Services Social care services help people who are ill, vulnerable, or disabled with day-to-day living. Definition
Services for Children Some children and young people may need temporary support from social care services for various reasons, such as protection, challenging Types of Physical Steps at entrances, buildings with multiple floors, small and cramped toilet facilities, no car parking or distant parking, uneven pavements and floors, narrow
and Young People behaviour, ill or incapable parents, or family problems. Types of social care services: foster care, residential care, youth work. Barriers doorways and corridors, busy or cluttered walkways, inaccessible toilets with low seats and no grab bars.
Foster Care Provides a family environment in own homes. Offers a safe and stable place. May be temporary or permanent. Supports growth and Effects of Physical Particularly affect those with reduced mobility or visual impairments.
development of the child with training and support for caregivers. Barriers
Minimizing Physical Provide parking spaces close to the entrance, install ramps or stair lifts, maintain even pavements and floors, ensure wide enough doorways and corridors for
Residential Care Similar to foster care, for children who can’t live at home. Staffed by professional staff in the home. Better for those with complex needs due Barriers wheelchair access, book appointments for less mobile patients at less busy times, install larger toilet facilities with higher seats and grab bars, use hoists to help
to structured environment and trained professionals. move physically disabled patients safely.
Youth Work Service for young people aged 11-25 in community settings. Organises activities supporting personal and social development. Helps build
confidence, self-esteem, communication, and life skills. 2 Sensory barriers Details
Services for Adults or Learning disabilities, sensory impairments, long-term health issues. Social care services: residential care, respite care, domiciliary care. Sensory Barriers Barriers that affect people with a sensory impairment, making it difficult to access services and information.
Children with Specific Definition Visual difficulties: small text, hard to read signs or maps, colour-coded signs, screens showing patient names.
Types of Sensory
Needs Barriers Hearing difficulties: noisy and dark reception areas, telephone booking systems, difficulty hearing instructions or medical terms.
Residential Care for Safe place for those with specific needs. 24-hour staff support for managing daily tasks. Provides personal care but not complex medical Effects of Sensory Make it difficult to get to a service, receive information clearly, or understand instructions.
Specific Needs care. Barriers
Respite Care Temporary relief for primary caregivers. Can take place at home, day care centres, or residential care homes. Provides time for caregivers to Overcoming Visual: Use large print leaflets, make signs bigger, design signs for colour blindness, use audio announcements.
rest and take care of themselves. Sensory Barriers Hearing: Quiet and well-lit areas, alternative booking methods, use of British Sign Language (BSL) interpreters, communication cards, hearing loops.
Domiciliary Care Helps with daily tasks and personal care at home. Provided by trained carers visiting the home. Can range from once a week to several visits
a day.
Services for Older Support for the effects of ageing, such as reduced strength, fitness, and mobility. Higher risk of health conditions like dementia, arthritis,
Adults sensory impairments, cardiovascular conditions. Types of care: residential care, domiciliary care.