Page 29 - Year 8
P. 29
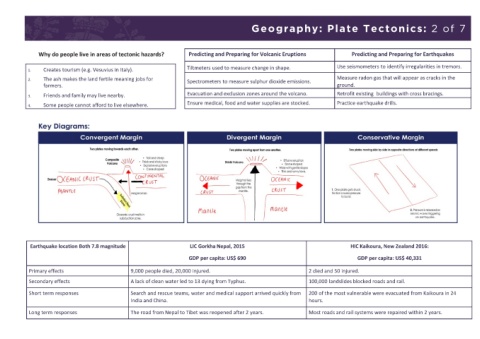
Geography: Plate Tectonics: 1 of 7 Geography: Plate Tectonics: 2 of 7
Continental Drift Why do people live in areas of tectonic hazards? Predicting and Preparing for Volcanic Eruptions Predicting and Preparing for Earthquakes
• The earth was initially a super 1. Creates tourism (e.g. Vesuvius in Italy). Tiltmeters used to measure change in shape. Use seismometers to identify irregularities in tremors.
continent called Pangea 250 2. The ash makes the land fertile meaning jobs for Spectrometers to measure sulphur dioxide emissions. Measure radon gas that will appear as cracks in the
million years ago. farmers. Evacuation and exclusion zones around the volcano. ground.
Retrofit existing buildings with cross bracings.
• Plates move a few centimetres a 3. Friends and family may live nearby. Ensure medical, food and water supplies are stocked. Practice earthquake drills.
year, but this adds up to 4. Some people cannot afford to live elsewhere.
thousands of kilometres over
millions of year.
• This movement is called Tectonic
drift.
Earthquake location Both 7.8 magnitude LIC Gorkha Nepal, 2015 HIC Kaikoura, New Zealand 2016:
GDP per capita: US$ 690 GDP per capita: US$ 40,331
Primary effects 9,000 people died, 20,000 injured. 2 died and 50 injured.
Secondary effects A lack of clean water led to 13 dying from Typhus. 100,000 landslides blocked roads and rail.
Short term responses Search and rescue teams, water and medical support arrived quickly from 200 of the most vulnerable were evacuated from Kaikoura in 24
India and China. hours.
Long term responses The road from Nepal to Tibet was reopened after 2 years. Most roads and rail systems were repaired within 2 years.