Page 56 - Year 9
P. 56
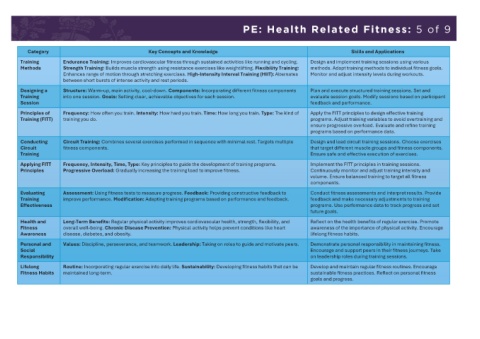
PE: Health Related Fitness: 5 of 9
Category Key Concepts and Knowledge Skills and Applications
Training Endurance Training: Improves cardiovascular fitness through sustained activities like running and cycling. Design and implement training sessions using various
Methods Strength Training: Builds muscle strength using resistance exercises like weightlifting. Flexibility Training: methods. Adapt training methods to individual fitness goals.
Enhances range of motion through stretching exercises. High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT): Alternates Monitor and adjust intensity levels during workouts.
between short bursts of intense activity and rest periods.
Designing a Structure: Warm-up, main activity, cool-down. Components: Incorporating different fitness components Plan and execute structured training sessions. Set and
Training into one session. Goals: Setting clear, achievable objectives for each session. evaluate session goals. Modify sessions based on participant
Session feedback and performance.
Principles of Frequency: How often you train. Intensity: How hard you train. Time: How long you train. Type: The kind of Apply the FITT principles to design effective training
Training (FITT) training you do. programs. Adjust training variables to avoid overtraining and
ensure progressive overload. Evaluate and refine training
programs based on performance data.
Conducting Circuit Training: Combines several exercises performed in sequence with minimal rest. Targets multiple Design and lead circuit training sessions. Choose exercises
Circuit fitness components. that target different muscle groups and fitness components.
Training Ensure safe and effective execution of exercises.
Applying FITT Frequency, Intensity, Time, Type: Key principles to guide the development of training programs. Implement the FITT principles in training sessions.
Principles Progressive Overload: Gradually increasing the training load to improve fitness. Continuously monitor and adjust training intensity and
volume. Ensure balanced training to target all fitness
components.
Evaluating Assessment: Using fitness tests to measure progress. Feedback: Providing constructive feedback to Conduct fitness assessments and interpret results. Provide
Training improve performance. Modification: Adapting training programs based on performance and feedback. feedback and make necessary adjustments to training
Effectiveness programs. Use performance data to track progress and set
future goals.
Health and Long-Term Benefits: Regular physical activity improves cardiovascular health, strength, flexibility, and Reflect on the health benefits of regular exercise. Promote
Fitness overall well-being. Chronic Disease Prevention: Physical activity helps prevent conditions like heart awareness of the importance of physical activity. Encourage
Awareness disease, diabetes, and obesity. lifelong fitness habits.
Personal and Values: Discipline, perseverance, and teamwork. Leadership: Taking on roles to guide and motivate peers. Demonstrate personal responsibility in maintaining fitness.
Social Encourage and support peers in their fitness journeys. Take
Responsibility on leadership roles during training sessions.
Lifelong Routine: Incorporating regular exercise into daily life. Sustainability: Developing fitness habits that can be Develop and maintain regular fitness routines. Encourage
Fitness Habits maintained long-term. sustainable fitness practices. Reflect on personal fitness
goals and progress.