Page 94 - Year 11
P. 94
PE: Component 2 Task 4: 7 of 8
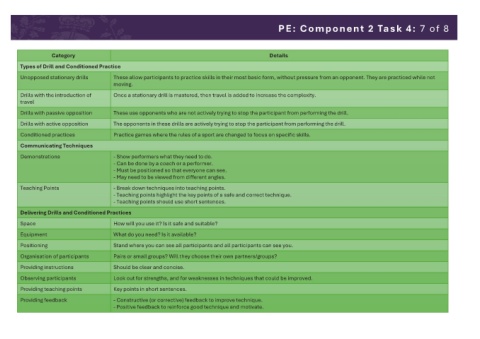
Category Details
Types of Drill and Conditioned Practice
Unopposed stationary drills These allow participants to practice skills in their most basic form, without pressure from an opponent. They are practiced while not
moving.
Drills with the introduction of Once a stationary drill is mastered, then travel is added to increase the complexity.
travel
Drills with passive opposition These use opponents who are not actively trying to stop the participant from performing the drill.
Drills with active opposition The opponents in these drills are actively trying to stop the participant from performing the drill.
Conditioned practices Practice games where the rules of a sport are changed to focus on specific skills.
Communicating Techniques
Demonstrations - Show performers what they need to do.
- Can be done by a coach or a performer.
- Must be positioned so that everyone can see.
- May need to be viewed from different angles.
Teaching Points - Break down techniques into teaching points.
- Teaching points highlight the key points of a safe and correct technique.
- Teaching points should use short sentences.
Delivering Drills and Conditioned Practices
Space How will you use it? Is it safe and suitable?
Equipment What do you need? Is it available?
Positioning Stand where you can see all participants and all participants can see you.
Organisation of participants Pairs or small groups? Will they choose their own partners/groups?
Providing instructions Should be clear and concise.
Observing participants Look out for strengths, and for weaknesses in techniques that could be improved.
Providing teaching points Key points in short sentences.
Providing feedback - Constructive (or corrective) feedback to improve technique.
- Positive feedback to reinforce good technique and motivate.